MS Health Bot Tutorial
This is a step-by-step guide to writing an Bot in C# using the Bot Framework Connector SDK .NET template. You will need to have collected some sleep data using a Microsoft Band and have had that synchronised up to the Microsoft cloud as this tutorial uses the Bot Framework to provide access to that data.
1) Install prerequisite software
- Visual Studio 2015 (latest update) - you can download the community version here for free: www.visualstudio.com
- Important: Please update all VS extensions to their latest versions Tools->Extensions and Updates->Updates
</blockquote>2) Download and install the Bot Application template
- Download the file from the direct download link here:
- Save the zip file to your Visual Studio 2015 templates directory which is traditionally in
“%USERPROFILE%\Documents\Visual Studio 2015\Templates\ProjectTemplates\Visual C#"
3) Open Visual Studio
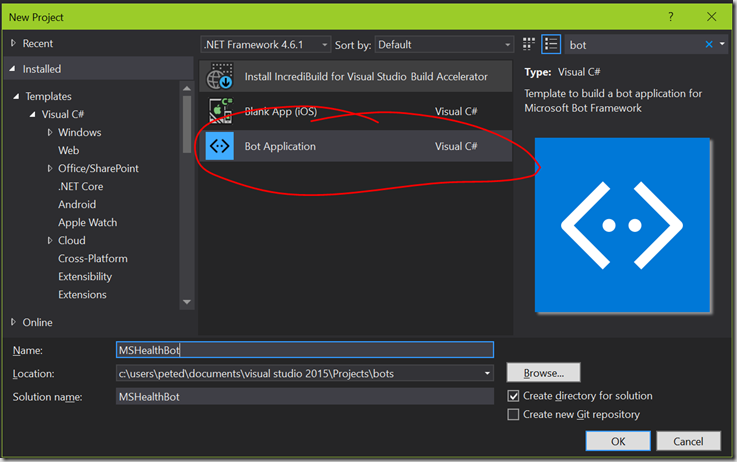
4) Select File > New > Project and you should see the dialog below. In the tree view on the left select Installed > Templates > Visual C# and click on the search box on the right and type bot
4) Select the Bot Application template and type in MSHealthBot as the Name and click OK
Visual Studio will now create and initialise your project.
The project that is created consists of an ASP.NET Web API project which is already set up with the Microsoft.Bot.Connector Nuget package and a MessagesController API end point with some boiler-plate Bot code.
ASP.NET Web API is an ideal platform for building RESTful applications on the .NET Framework
NuGet is the package manager for the Microsoft development platform including .NET
This represents the back-end of your bot and where the business logic code for your bot will all reside. The other main part of the system would be the bot client and that would represent the interface to your end-user. An example of a bot client might be Skype or Slack where the user might type in questions for your bot to answer or it could a voice recognition agent; ultimately your bot can work with any client. The Microsoft Bot Framework provides us with an emulator so that we can develop and test our bot.so the next step is to become familiar with its usage.
To install the Bot Framework Emulator, download it from here.
To set up the Bot Framework Emulator (please see http://docs.botframework.com/connector/getstarted/#getting-started-in-net for installation and set up instructions).
Note that the link between the bot you are currently developing and the emulator are the App ID and App Secret values which you find in your project’s Web.Config file:
This ensures that your bot can be authenticated but for the purpose of this tutorial you can use them as they are. Please follow the next steps to get the default bot up and running in the Bot Emulator:
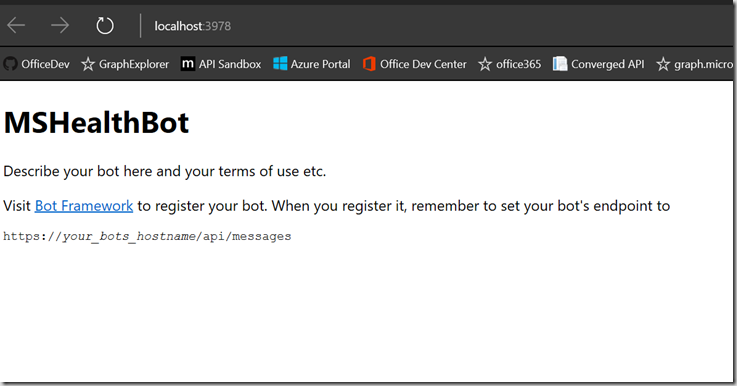
1) From Visual Studio select Debug > Start Debugging or press F5. This will start an instance of IISExpress on your machine which will locally host your bot and will open a browser window. This should look like the following:
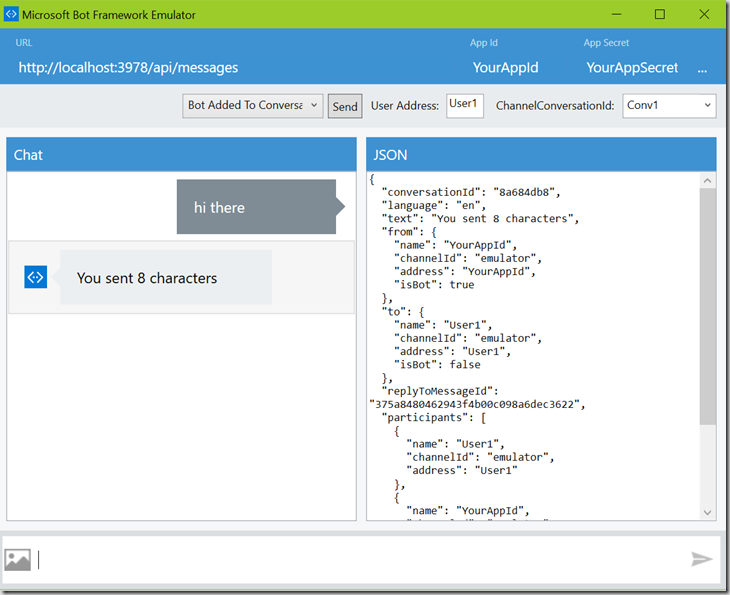
2) Whilst that is running, run up the emulator and ensure that it is pointing to the correct localhost url including port number and with the path /api/messages and the App ID and App Secret set correctly. Compare with:
3) Type ‘hi there’ into the emulator’s chat window and you should get the reply ‘you sent 8 characters’ and you will see some JSON metadata in the right-hand pane which is data from the client that you will have available from within your bot code. The reply you see comes directly from the code in your bot; compare with the default bot implementation.
Now, let’s start to build up our own logic onto this baseline. The project will consume two external services; the Microsoft Health API and LUIS (Language Understanding Intelligent Service) so let’s consider each in turn:
Microsoft Health API
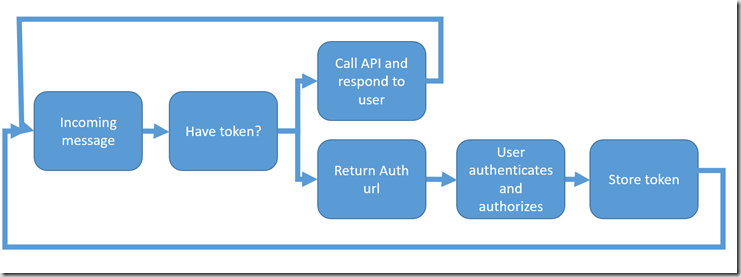
This is an API over data from your Microsoft Band. The way that it works is that when you use your Microsoft Band to monitor your sleep or running it stores the data locally in it’s flash memory. When you are near your mobile phone the data is synchronised to the phone and from the phone synchronised up to the Microsoft cloud. From there you can access your data via this web dashboard or via the MS Health API. In order to access your data via the API you need to retrieve an OAuth 2 access token using a typical OAuth 2 authorisation code flow which typically requires browser-style redirects (see here for more details). This poses a problem for a bot as it doesn’t have a browser window. None of the examples I had seen up to this point mentioned auth in terms of how would a bot user authenticate and authorise access to their data. Azure Active Directory auth allows web-browser-free auth using the OAuth2 client credentials flow to authorise an app but applications and APIs using Windows Live style application registration do not. Microsoft Health Cloud API uses “Microsoft account (formerly Live Id)” token-based OAuth (Open Authorization) 2.0 authentication and more specifically the OAuth 2.0 authorisation code flow which requires browser-style redirects which are not provided for by a typical Bot client. Since I specifically wanted to call the Health API this requires the user to give consent to access for the calling app – in order to support this we can implement the following flow:
Your bot will need to be registered as an OAuth 2.0 client:
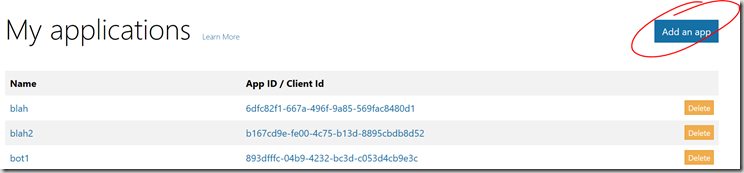
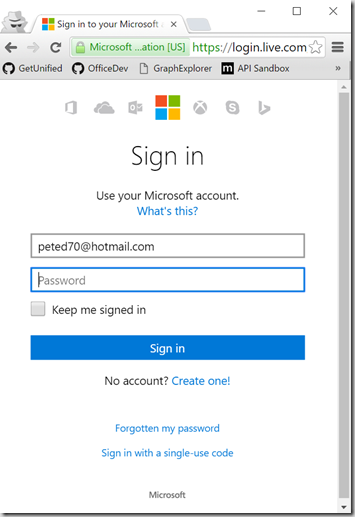
1) Navigate to the Microsoft account developer center https://account.live.com/developers/applications in a browser. Click on Add App.
2) Create an app and call it MSHealthBot
3) Make a note of the Application ID
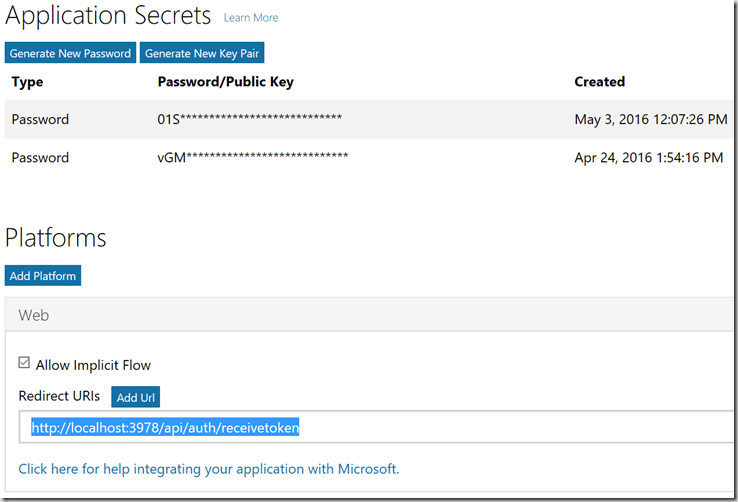
4) Generate a new password and make a note of it
5) Click Add Platform and select Web
6) Enter a Rediirect Uri – use your bot’s base url and add /api/auth/receivetoken to it, e.g. http://localhost:3978/api/auth/receivetoken (we will implement this endpoint in the bot Web API).
7) Click Live SDK support
8) Save the settings
9) Copy the following code into your Global.asax.cs file:
10) Right-click the Controllers folder in the Solution Explorer and choose Add > Class and name it AuthController. Replace the new files contents with the code below:
Find any red squiggles in the file, put your cursor on them and press CTRL + . to resolve any missing namespace usings.
Let’s take a moment to understand the code we just pasted in
- the code we put into global.asax.cs is simply a convenient way to store the auth token in memory on the server. In a production system we could use secure cloud storage.
- the AuthController code provides an endpoint to initiate an OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow and also a redirect uri to receive an auth code which can be exchanged for an access token
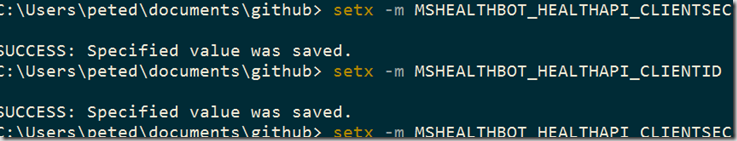
11) The code also relies on two other environment variables being set: MSHEALTHBOT_HEALTHAPI_CLIENTID & MSHEALTHBOT_HEALTHAPI_CLIENTSECRET which can be copied from your app registration. To set the variables from your dev machine you can use the setx command from the command prompt with the value as the last parameter:
Using this technique set the MSHEALTHBOT_HEALTHAPI_CLIENTID variable to the App ID you noted down from the earlier step and set the MSHEALTHBOT_HEALTHAPI_CLIENTSECRET to the App Secret we also noted earlier.
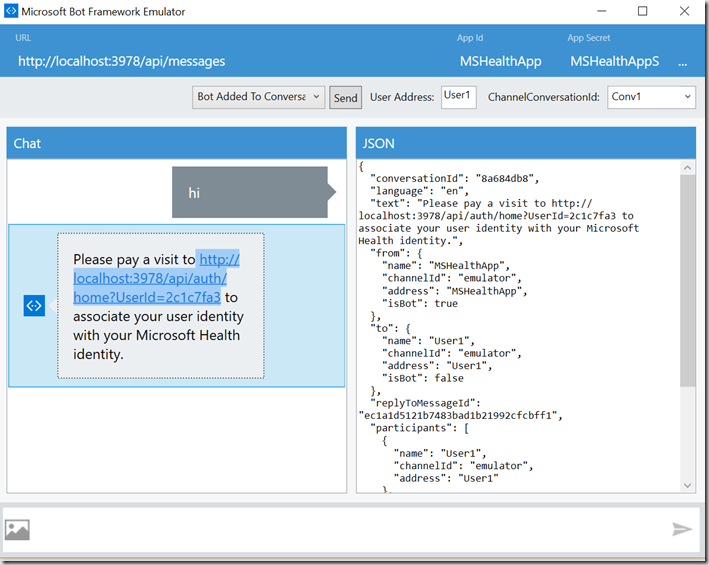
If the app is not authorised the bot will reply with a link
User clicks the link which will take them to authorisation server passing a unique ID from the Bot Framework
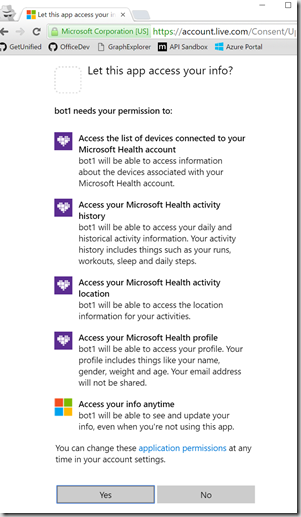
The user authenticates by logging in and then gives consent through the standard OAuth consent dialog
The unique user id is passed to the redirect uri which I have implemented as part of my Bot Web API along with the Health API access token
The bot Web API stores the access token and it’s related unique user id together
Subsequent calls to the Health API can use the access token to make calls (will stop working if the access token expires as I didn’t implement refresh tokens)
Subsequently, we have the access token which we can send in the auth header for requests to the Health API.
Health API Helpers
We need some code to call the Health API so let’s bring that in next:
1) Right-click on your project and select Add > New Folder and name the folder Models
2) Copy the code from here MS Health Model Code and paste it into a new file named Model.cs inside the Models folder
3) Next, add the two helper methods below which wrap the calls to the Health APIs:to your MessagesController class
Find the AuthenticationHeaderValue reference, put your cusrsor over it and press CTRL and . and then resolve the namespace
4) Finally add the following private member variable to your MessagesController class
LUIS
To be effective a bot needs to allow the user to communicate using language which is natural and as we know language can sometimes be imprecise, ambiguous and nuanced. Trying to create a fixed grammar that could deal with these aspects would soon become very complex and hard to maintain. Instead we can leverage machine learning techniques and LUIS provides us with a way to do this which is very easy to set up and use.
1) Download the JSON file here https://github.com/peted70/ms-health-bot/blob/2bbdbd7ed311db0362f1f6d9c95ee489dee8544a/assets/MSHealthBot.json
2) Navigate to https://www.luis.ai
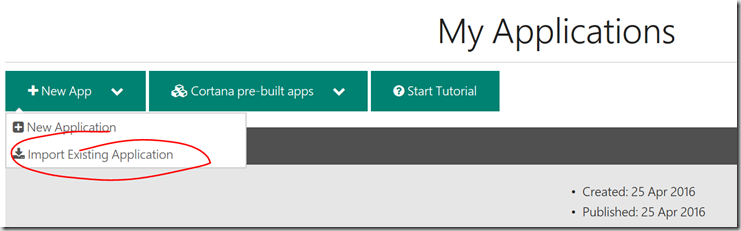
3) Choose New App with the option Import Existing Application
4) Upload the JSON file here
Note that this will import a LUIS model that I have already trained – for details about how this was done please see my previous post.
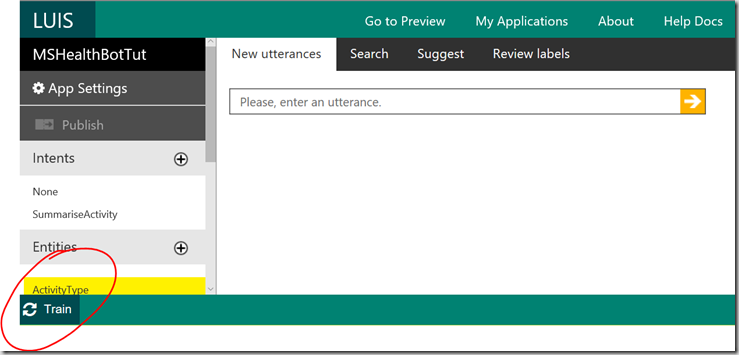
5) Once imported you will need to train the model so select your app and at the lower left of it’s property page click the train button
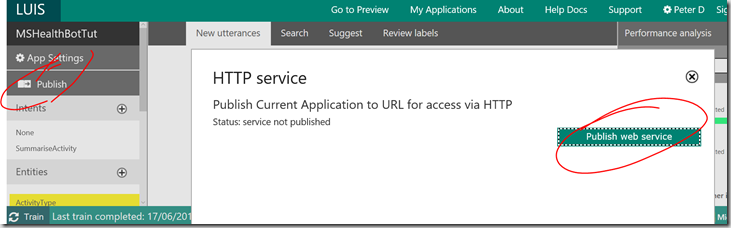
6) Once trained the publish button on the left will become enabled. Click publish followed by publish web service
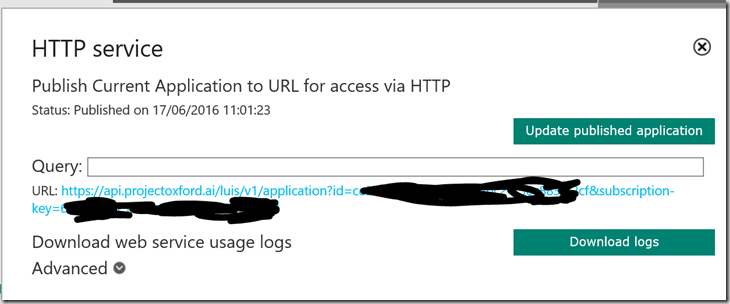
7) Once published you will get back a url at which your LUIS service can be accessed. The url will include an id and a subscription key – these are used to monitor usage – if your key becomes compromised you can generate a new one here.
8) That’s it – you now have a web service which will enable you to carry out natural language processing and will recognise entities associated with the Health APIs such as sleep, run, walk, etc. and also to recognise points in time and time ranges such as last week, or a year ago, etc.
Calling the LUIS Web Service
1) Open your MessageController.cs class and place the following method somewhere inside the MessageController class:
Note that the App ID and App Secret for the LUIS web service are again accessed as environment variables so you will need to set them using setx as done previously for the Health API ID and Secret (see above).
Bot Implementation
Now we have all of the moving parts to implement our health bot
1) Introduce the in-memory credential store into the MessageController class – remove the existing contructor and paste the following code into the class:
2) Replace the whole body of the Post method with:
This implements our auth logic described earlier and will return an auth url to the user if no token is stored for them
3) Next we will install the NodaTime Nuget package to help us to parse out some of the time formats used by the Health API responses. So right-click the References node in the Solution Explorer and choose Manage Nuget Packages. In the Nuget dialog that will open Click on the Browse tab and ensure that Include Pre-release is checked. Then search for NodaTime, click the list item and then choose the version 2.0.0-alpha20150728 and click install.
4) Find the TODO comment from the previous step and replace it with the following code.
The last piece of code implements one possible scenario using the sleep activity however it is not difficult to see how this could be extended to work for all of the activities supported by the Health API – that is left as an exercise for the reader!
Summary
This tutorial has illustrated how to put together a real-world, useful bot not just be providing a text input interface to an API but allowing the user to use their natural voice input to query the aggregated data. Hopefully, this will leave you with some ideas about how to implement a bot for your own scenario.




Comments